Content
- 1 What Core Requirements Should Energy-Saving Pneumatic Vacuum Generators Meet for Material Handling?
- 2 Which Key Parameters Determine the Energy Efficiency of Pneumatic Vacuum Generators?
- 3 How to Match Vacuum Generators to Different Material Handling Scenarios?
- 4 What Energy-Saving Technologies Are Integrated into Advanced Vacuum Generators?
- 5 How to Verify the Actual Energy-Saving Effect and Reliability of Vacuum Generators?
What Core Requirements Should Energy-Saving Pneumatic Vacuum Generators Meet for Material Handling?
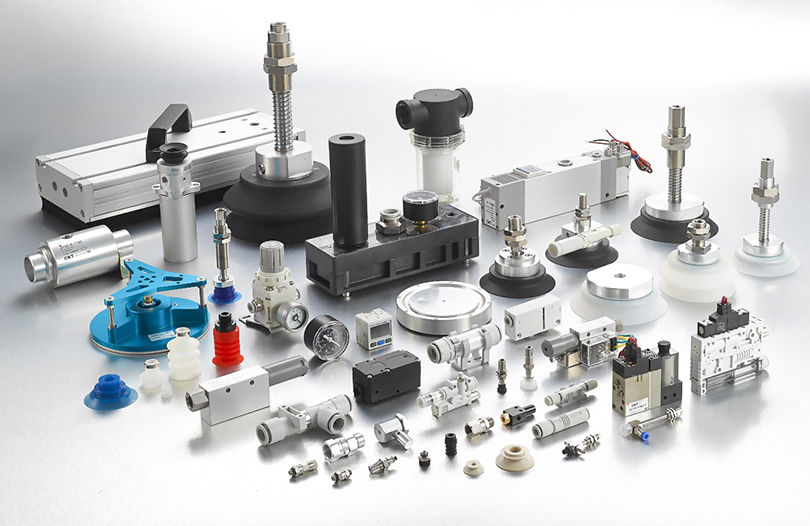
Material handling scenarios—from lightweight packaging transfer to heavy workpiece lifting—demand pneumatic vacuum generators that balance suction performance, energy efficiency, and reliability. The core requirements include stable vacuum pressure (typically -60 kPa to -90 kPa) to ensure firm gripping, air consumption below 50 L/min (at standard conditions) for energy savings, and rapid response time (≤0.3 seconds) to improve handling efficiency. Additionally, compatibility with diverse materials (porous, non-porous, irregularly shaped) and resistance to dust or debris in industrial environments are essential. These requirements stem from the need to reduce compressed air costs—accounting for 15-30% of industrial energy consumption—while avoiding material damage or handling failures.
Which Key Parameters Determine the Energy Efficiency of Pneumatic Vacuum Generators?
Three critical parameters directly influence energy-saving performance: air consumption, vacuum flow rate, and energy recovery design. Air consumption reflects the volume of compressed air used per cycle; generators with optimized nozzle structures (such as multi-stage venturi designs) can reduce consumption by 30-40% compared to traditional single-nozzle models. Vacuum flow rate (measured in L/min) determines the speed of air extraction—sufficient flow rate ensures quick vacuum buildup even for porous materials like cardboard. Energy recovery systems, such as integrated check valves or pressure retention mechanisms, prevent air waste by maintaining vacuum pressure during short pauses in handling. Selectors must also consider the generator’s operating pressure range (0.4-0.7 MPa) to match existing compressed air systems without additional energy input.
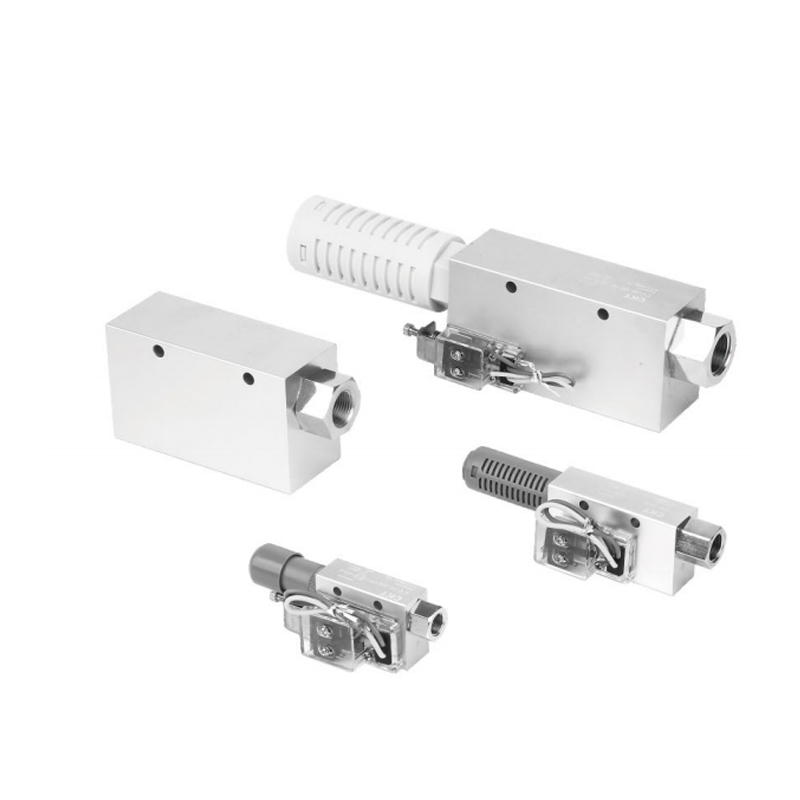

How to Match Vacuum Generators to Different Material Handling Scenarios?
Scenario-specific matching is crucial to avoid over-energy consumption or insufficient performance. For lightweight, non-porous materials (e.g., plastic sheets, metal foils), compact generators with low air consumption (20-30 L/min) and moderate vacuum pressure (-70 kPa to -80 kPa) are ideal. Heavy-duty applications (e.g., lifting metal components, concrete slabs) require high-flow generators (≥80 L/min) with strong vacuum pressure (-85 kPa to -90 kPa) and reinforced suction cups to distribute weight evenly. Porous materials (e.g., wood panels, foam) demand generators with high flow rates to compensate for air leakage, while intermittent handling scenarios benefit from generators with automatic shutoff functions to stop air flow when vacuum is maintained. Environmental factors—such as temperature (-10℃ to 60℃) and humidity—also influence selection to ensure long-term stability.
What Energy-Saving Technologies Are Integrated into Advanced Vacuum Generators?
Modern pneumatic vacuum generators adopt multiple technologies to minimize energy use. The multi-stage venturi principle, which uses sequential nozzles to amplify vacuum pressure with lower air input, is a core innovation—this design reduces air consumption by 25-40% compared to single-stage models. Intelligent pressure control systems, equipped with pressure sensors and proportional valves, adjust air flow in real time based on material weight and porosity, avoiding unnecessary energy waste. Additionally, energy recovery valves capture and reuse residual compressed air from the exhaust, while low-friction internal components reduce pressure loss during operation. Some generators also feature sleep modes that deactivate air flow when not in use, further cutting energy consumption in batch handling processes.
How to Verify the Actual Energy-Saving Effect and Reliability of Vacuum Generators?
Practical verification requires evaluating both laboratory data and on-site performance. Key metrics include specific energy consumption (kWh per 1,000 cycles) and vacuum retention time—generators with specific energy consumption below 0.5 kWh/1,000 cycles are considered highly energy-efficient. On-site tests should simulate real handling conditions, measuring air consumption under different loads and material types to ensure consistency with manufacturer specifications. Reliability verification involves endurance testing (≥10,000 continuous cycles) to check for component wear or performance degradation. Additionally, noise levels (≤75 dB) and maintenance requirements (e.g., filter replacement intervals) should be assessed, as frequent maintenance can indirectly increase energy and operational costs.