Pneumatic air cylinders are widely used in mechanical equipment, production lines, robots, and other fields. They use compressed air to drive piston movement, achieving precise linear motion, thus playing a crucial role in ensuring industrial production efficiency and equipment stability. However, under long-term, high-frequency use, pneumatic cylinders may experience problems such as wear and leakage, affecting equipment operating efficiency and service life. To extend the service life of pneumatic cylinders, regular maintenance and care are essential.
1. Regularly Check the Operating Status of the Pneumatic Cylinder
Long-term operation of pneumatic cylinders can lead to wear and tear of components, especially key components such as pistons, seals, and guide rods. Therefore, regularly checking the operating status of the pneumatic cylinder is very necessary.
Inspection items include:
Cylinder appearance inspection: Check the cylinder housing for any obvious wear, cracks, or deformation. Any physical damage may affect the cylinder's sealing performance and operating stability.
Piston movement inspection: Confirm that the piston moves smoothly inside the cylinder and that there is no sticking. Normal piston movement ensures the efficient operation of the pneumatic cylinder.
Cylinder airtightness inspection: Check the cylinder for air leaks. This can be done by applying soapy water or using a dedicated leak detection instrument to check for gas leaks at the cylinder ports and seals.
Solutions:
If the cylinder housing is found to be cracked or deformed, the cylinder should be replaced immediately.
If the piston movement is stuck, it may be due to dust, impurities, or poor lubrication. The lubrication system needs to be cleaned and checked.
If a leak is found in the cylinder, check the sealing of the seals and end caps, and replace them if necessary.

2. Maintain the Cylinder's Lubrication System
The lubrication system of a pneumatic cylinder is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear. Lack of lubrication will cause excessive friction between the piston and seals, accelerating component wear and ultimately leading to cylinder failure. Therefore, regular inspection and maintenance of the lubrication system are very important.
Lubrication precautions:
Lubricant selection: Choose a lubricant suitable for the working environment and gas conditions of the pneumatic cylinder. Generally, pneumatic cylinders require low-friction, anti-oxidant lubricants to reduce wear. Oil Level Monitoring: Ensure the proper amount of lubricating oil in the cylinder. Too much or too little lubricant will affect the cylinder's working efficiency.
Regular Lubrication: Regularly add lubricating oil, especially when the cylinder is frequently in operation, to maintain proper lubrication.
Solutions:
Use specialized pneumatic lubricating oil to lubricate the cylinder, avoiding the use of unsuitable greases.
Regularly check the oil level to ensure the cylinder remains properly lubricated at all times.
For cylinders operating in special environments such as high temperature and high pressure, choose specially designed lubricants to improve durability.
3. Preventing Contaminants from Entering the Cylinder
The normal operation of a cylinder requires a clean gas supply. Dust, impurities, and moisture in the air can easily cause cylinder damage, seal failure, and the accumulation of wear particles inside the cylinder, thus shortening its service life.
Measures to Prevent Contamination:
Install filters: Install high-efficiency air filters at the air source inlet to filter out moisture, dust, and impurities from the air. For compressed air systems, use a dryer to remove moisture from the air.
Regularly clean the cylinder: Regularly clean the outside of the cylinder, especially in dusty environments, to prevent contaminants from entering through external contact.
Regularly check the air supply system: Check the working condition of air pipes, connectors, filters, and other components to ensure that no contaminants enter the cylinder.
Solutions:
Install suitable air filters and regularly replace the filter elements.
Regularly check and clean the air source system to ensure clean air.
Avoid using air with oil mist or moisture, ensuring a clean and contaminant-free air source.
4. Controlling the Operating Pressure of the Pneumatic Cylinder
While pneumatic cylinders can provide stronger power output when operating under high pressure, this also accelerates wear and damage to the cylinder. Both excessively high and low pressures will affect the working efficiency and service life of the pneumatic cylinder.
Measures to Control Air Pressure:
Regularly check the air source pressure: The operating pressure of the pneumatic cylinder should be set according to its specifications and application environment. Excessively high pressure will overload the cylinder and increase wear; while excessively low pressure will affect the cylinder's working efficiency.
Use a pressure regulator: Install a pressure regulator in the air source system to ensure that the cylinder's operating pressure is always maintained within a reasonable range.
Solution:
Install a pressure regulator and pressure reducing valve to ensure stable air source pressure.
Avoid operating the cylinder at excessively high or low pressures for extended periods.
5. Regularly inspect seals and valves
The seals and valves of pneumatic cylinders play a crucial role in ensuring the cylinder's airtightness and accurate operation. With increased use, seals may wear out or age, leading to poor airtightness and air leaks.
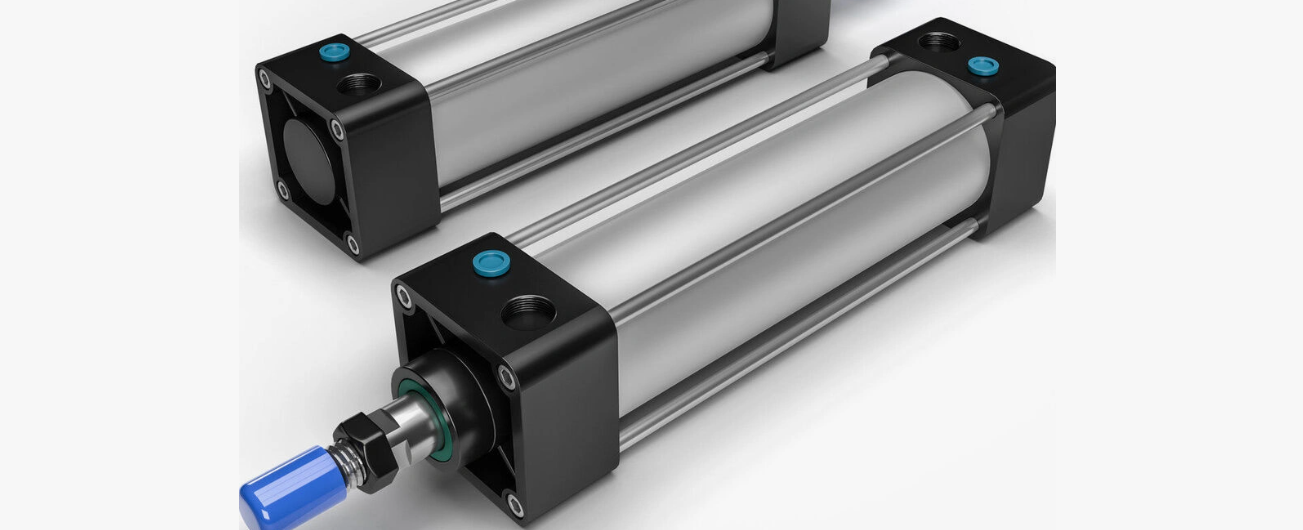

Measures for inspecting and replacing seals:
Regularly inspect seals: Regularly check the cylinder end caps, piston seals, and other seals for wear or aging. Damaged seals can lead to air leaks and reduced working efficiency.
Check valve operation: Check if the cylinder valves are working properly. Valve malfunctions can cause the cylinder to operate sluggishly or not as expected.
Replace damaged seals promptly: If seals are found to be aged, worn, or damaged, replace them promptly to ensure the normal operation of the cylinder.
Solution:
Regularly inspect seals and valves, especially under high-load conditions, to ensure they are in good condition.
Use high-quality sealing materials suitable for pneumatic cylinder operation to extend the lifespan of the seals.
Replace seals regularly to avoid cylinder malfunctions caused by poor sealing.